Running Buildkite Agent on Google Cloud Platform
This page references the out-of-date Buildkite Agent v2.
For docs referencing the Buildkite Agent v3, see the latest version of this document.
The Buildkite Agent can be run on Google Cloud Platform. For fine control over long–lived agents, you might like to run the agent using individual VM instances on Google Compute Engine. Or run Docker–based builds using a scalable cluster of agents on the Google Kubernetes Engine using Kubernetes.
Running the agent on Google Compute Engine
To run the agent on your own Google Compute Engine instance use whichever installer matches your instance type. For example:
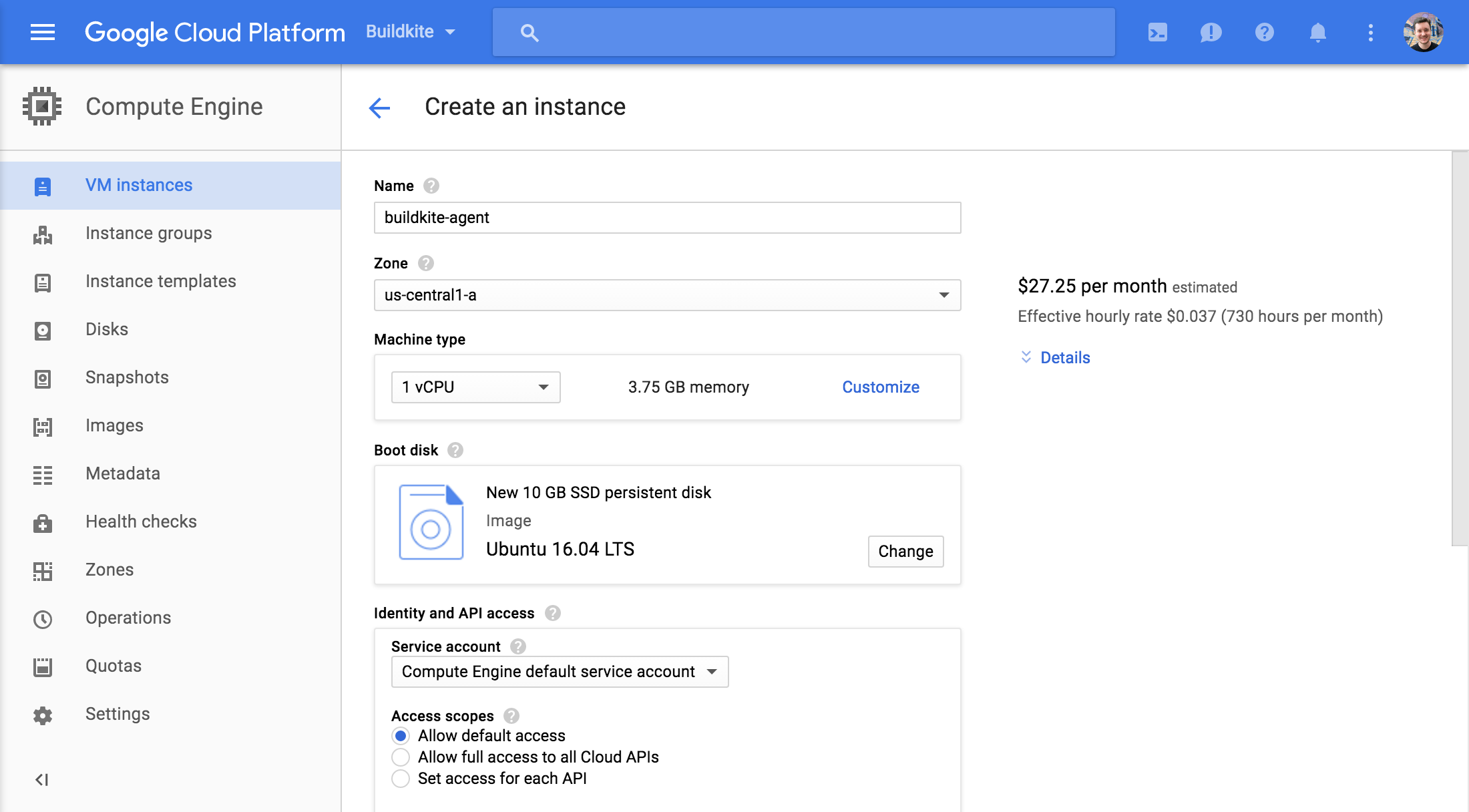
Launch an instance using the latest Ubuntu LTS image through the console:
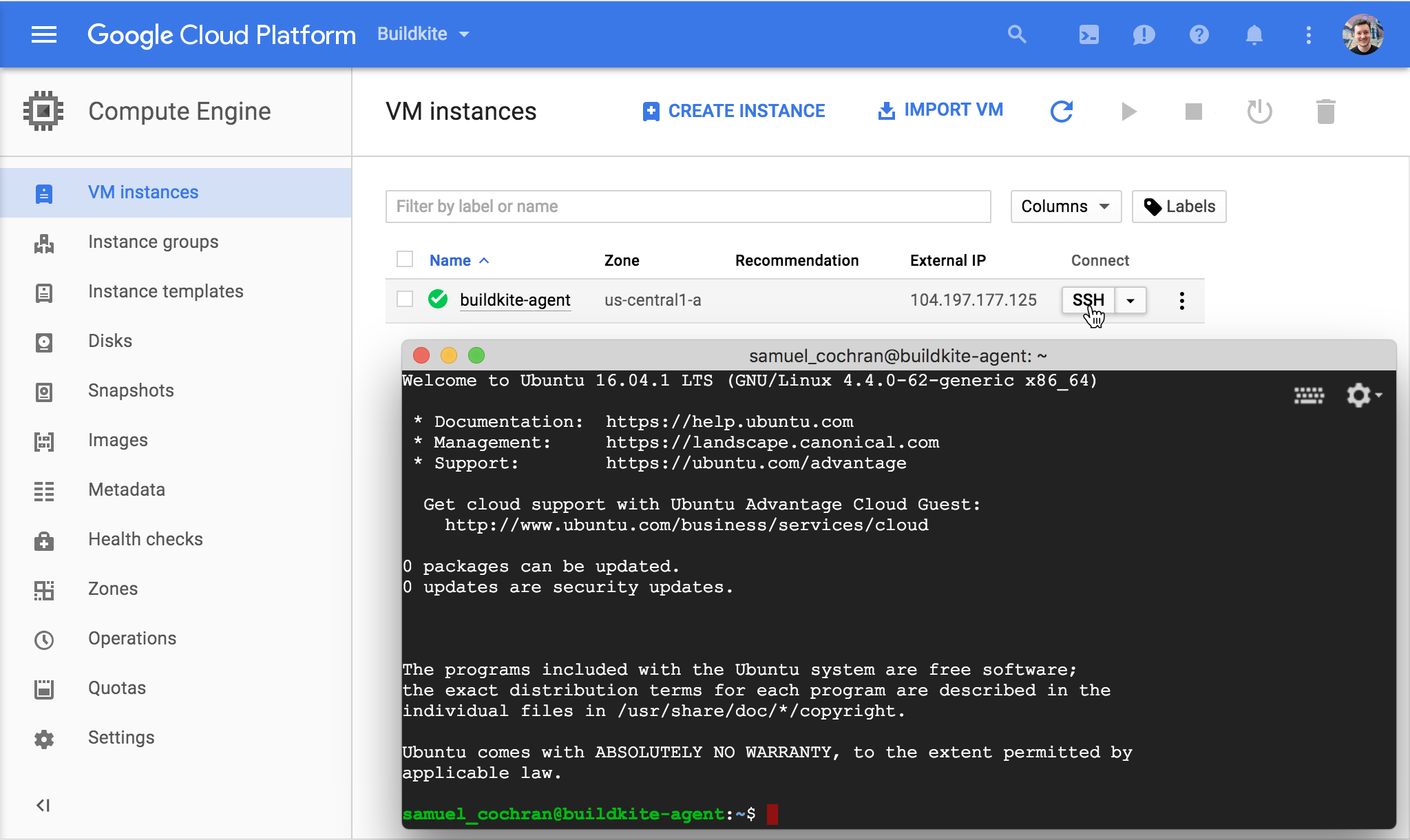
Connect using SSH:
Follow the setup instructions for Ubuntu.
Running the agent on Google Kubernetes Engine
Google Kubernetes Engine can run the agent as a Docker container using Kubernetes. To run Docker–based builds, ensure the container is started with a privileged security context and mount the Docker socket and binary as volumes. For example:
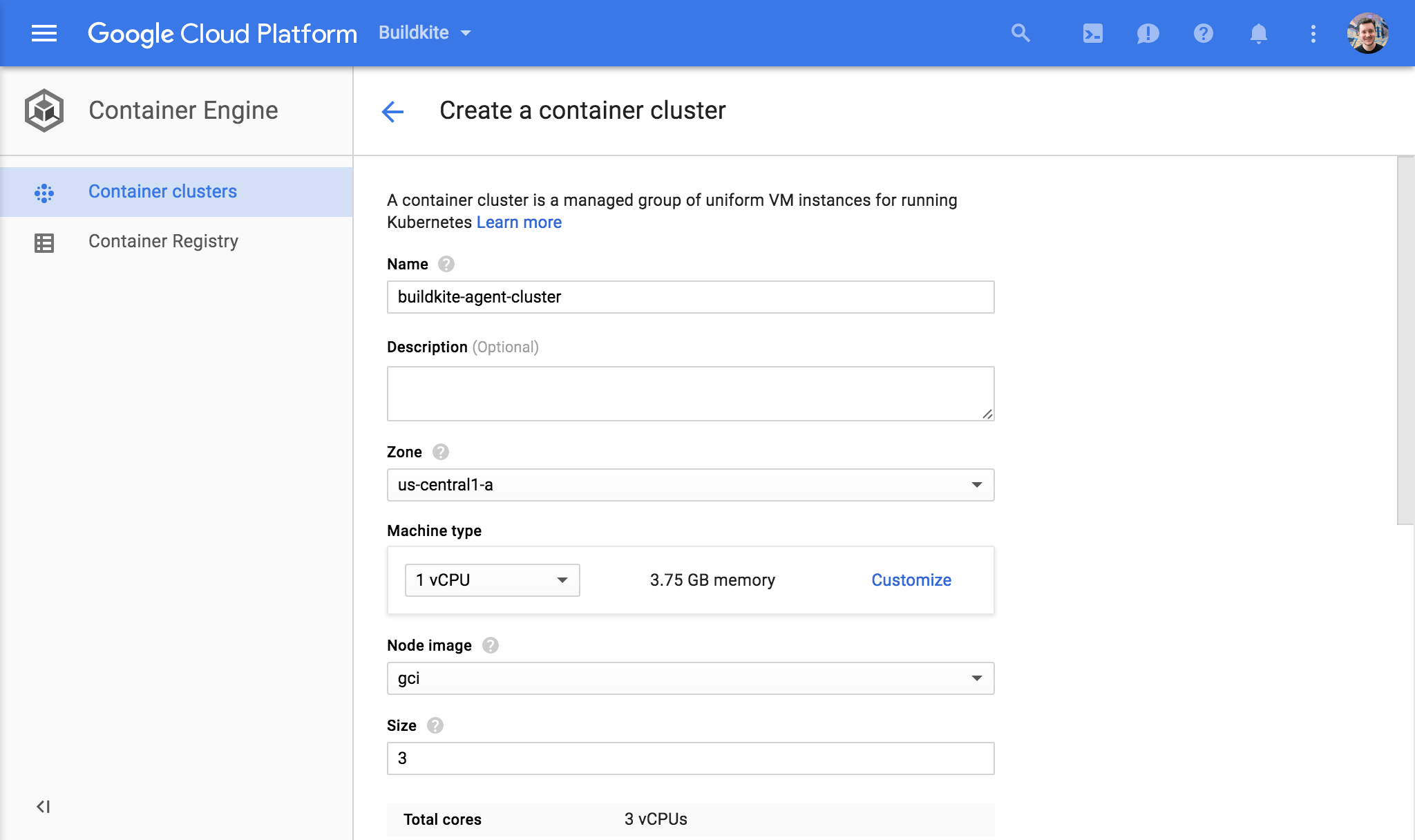
Start a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster through the console:
Open Google Cloud Shell, or your own console with gcloud installed and authenticated. You'll need to configure kubectl to talk to your new cluster. The console includes a "Connect" button which shows the exact command to run:
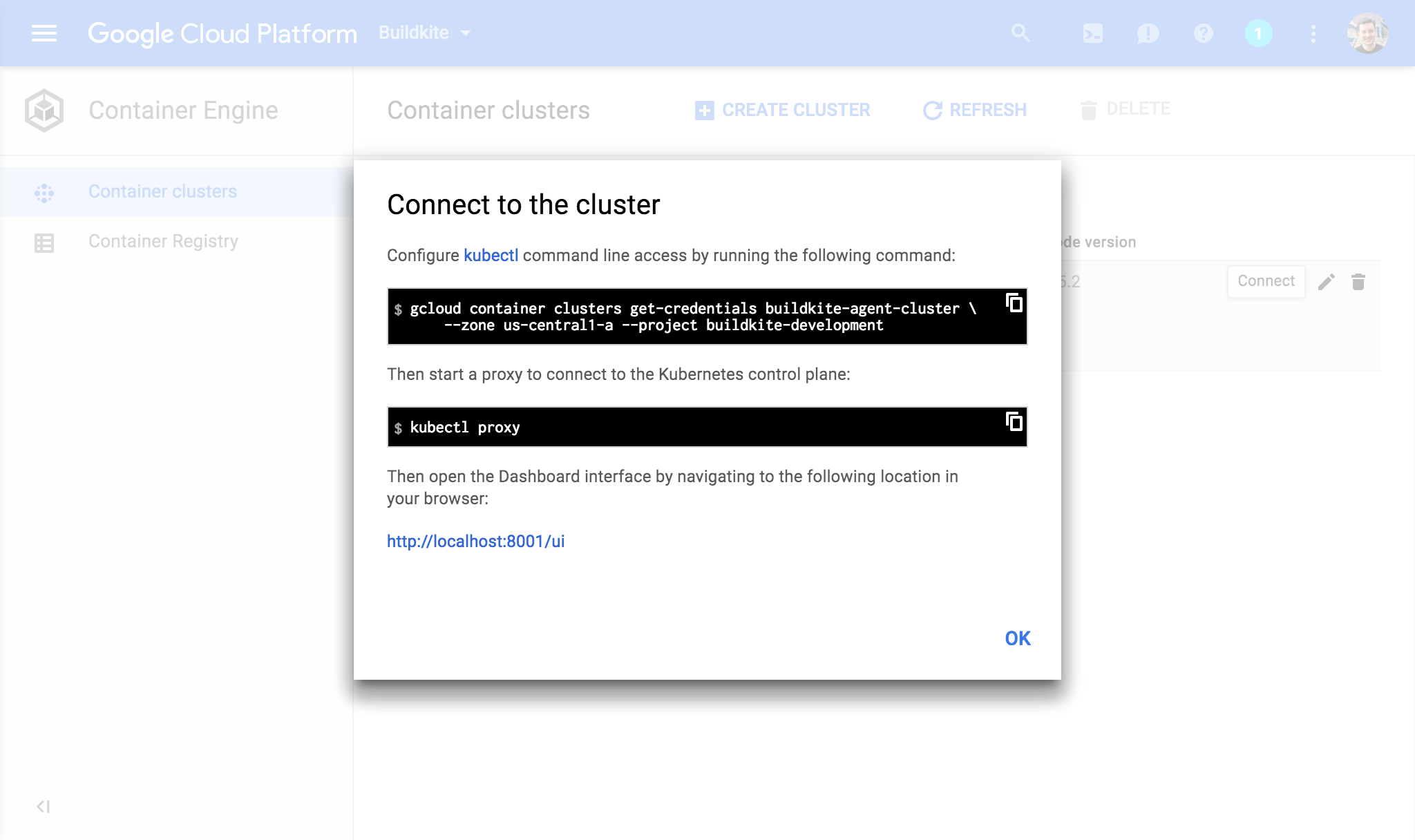
Running it should look like this, with your details in the right places:
$ gcloud container clusters get-credentials INSERT-YOUR-CLUSTER-NAME \
--zone INSERT-YOUR-ZONE --project INSERT-YOUR-PROJECT
Fetching cluster endpoint and auth data.
kubeconfig entry generated for YOUR-CLUSTER-NAME
Double check it's running by taking a look at the cluster info:
$ kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes master is running at https://123.45.67.89
GLBCDefaultBackend is running at https://123.45.67.89/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/default-http-backend
Heapster is running at https://123.45.67.89/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/heapster
KubeDNS is running at https://123.45.67.89/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns
kubernetes-dashboard is running at https://123.45.67.89/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/kubernetes-dashboard
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
Create a secret with your agent registration token:
$ kubectl create secret generic buildkite-agent --from-literal token=INSERT-YOUR-AGENT-TOKEN-HERE
secret "buildkite-agent" created
Create a deployment to start an agent:
$ cat | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: buildkite-agent
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: buildkite-agent
spec:
containers:
- name: buildkite-agent
image: buildkite/agent
imagePullPolicy: Always
securityContext:
privileged: true
env:
- name: BUILDKITE_AGENT_TOKEN
valueFrom: {secretKeyRef: {name: buildkite-agent, key: token}}
volumeMounts:
- name: docker-binary
mountPath: /usr/bin/docker
- name: docker-socket
mountPath: /var/run/docker.sock
volumes:
- name: docker-binary
hostPath: {path: /usr/bin/docker}
- name: docker-socket
hostPath: {path: /var/run/docker.sock}
# (press Control-D)
deployment "buildkite-agent" created
Verify this started a pod running the agent:
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
buildkite-agent-3220167863-dtzcf 1/1 Running 0 30s
And verify that the agent has registered successfully in the logs:
$ kubectl logs buildkite-agent-3220167863-dtzcf
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
| | (_) | | | | (_) | | |
| |__ _ _ _| | __| | | ___| |_ ___ __ _ __ _ ___ _ __ | |_
| '_ \| | | | | |/ _` | |/ / | __/ _ \ / _` |/ _` |/ _ \ '_ \| __|
| |_) | |_| | | | (_| | <| | || __/ | (_| | (_| | __/ | | | |_
|_.__/ \__,_|_|_|\__,_|_|\_\_|\__\___| \__,_|\__, |\___|_| |_|\__|
__/ |
http://buildkite.com/agent |___/
2017-02-16 03:34:10 NOTICE Starting buildkite-agent v2.3.2 with PID: 5
2017-02-16 03:34:10 NOTICE The agent source code can be found here: https://github.com/buildkite/agent
2017-02-16 03:34:10 NOTICE For questions and support, email us at: hello@buildkite.com
2017-02-16 03:34:10 INFO Registering agent with Buildkite...
2017-02-16 03:34:11 INFO Successfully registered agent "buildkite-agent-3220167863-1cvr5" with meta-data []
2017-02-16 03:34:11 INFO Connecting to Buildkite...
2017-02-16 03:34:11 INFO Agent successfully connected
2017-02-16 03:34:11 INFO You can press Ctrl-C to stop the agent
2017-02-16 03:34:11 INFO Waiting for work...
You're successfully running a Buildkite Agent!
Running more than one agent
To run more than one agent you can increase replicas:
$ kubectl scale --replicas=5 deployment buildkite-agent
deployment "buildkite-agent" scaled
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
buildkite-agent-3220167863-0m269 1/1 Running 0 24s
buildkite-agent-3220167863-0mtps 1/1 Running 0 24s
buildkite-agent-3220167863-1cvr5 1/1 Running 0 3m
buildkite-agent-3220167863-9psz9 1/1 Running 0 24s
buildkite-agent-3220167863-m3nm2 1/1 Running 0 24s
Authenticating to private repositories
To run builds from private repositories you can store an SSH key for the agent in a secret and map it into the containers:
# Use an existing key pair, or generate a new one with something like:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048 -N "" -C buildkite-agent -f id_rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Your identification has been saved in id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in id_rsa.pub.
...
# Create a secret containing the ssh keys:
$ kubectl create secret generic buildkite-agent-ssh \
--from-file id_rsa=id_rsa \
--from-file id_rsa.pub=id_rsa.pub
secret "buildkite-agent-ssh" created
# Change the spec to include new volumes to map the ssh key into place (because
# this is Docker the git and ssh processes are running as root):
$ kubectl edit deployment buildkite-agent
...
spec:
containers:
- ...
volumeMounts:
- name: ssh-keys
mountPath: /root/.ssh/id_rsa
subPath: id_rsa
- name: ssh-keys
mountPath: /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
subPath: id_rsa.pub
...
volumes:
- name: ssh-keys
secret:
secretName: buildkite-agent-ssh
defaultMode: 0400
...
If you git clone over HTTPS (for example using a GitHub API token) you could mount a git-credentials file instead:
spec:
containers:
- ...
volumeMounts:
- name: git-credentials
mountPath: /root/.git-credentials
subPath: .git-credentials
...
volumes:
- name: git-credentials
secret:
secretName: buildkite-agent-git-credentials
defaultMode: 0400
...
Further configuration
To configure the agent further you can create a config map and volume mount it over the default agent configuration file in /buildkite/buildkite-agent.cfg.
To add agent hooks add another config map and volume mount them into /buildkite/hooks/.
To add container startup scripts, add another config map with files and volume mount them into /docker-entrypoint.d/. Note: scripts in this directory must not have any periods (.) or any file extensions since they are run by the run-parts util.
See our Docker setup instructions for more details on configuring and customizing the Buildkite Agent running in Docker.
Uploading artifacts to Google Cloud Storage
You can upload the artifacts created by your builds to your own Google Cloud Storage bucket. Configure the agent to target your bucket by exporting the following environment variables using an environment agent hook (this can not be set using the Buildkite web interface, API, or during pipeline upload):
export BUILDKITE_ARTIFACT_UPLOAD_DESTINATION="gs://my-bucket/$BUILDKITE_PIPELINE_ID/$BUILDKITE_BUILD_ID/$BUILDKITE_JOB_ID"
Make sure the agent has permission to create new objects. If running on Google Compute Engine or Google Kubernetes Engine you can grant Storage Write permission to the instance or cluster, or restrict access more specifically using a service account.